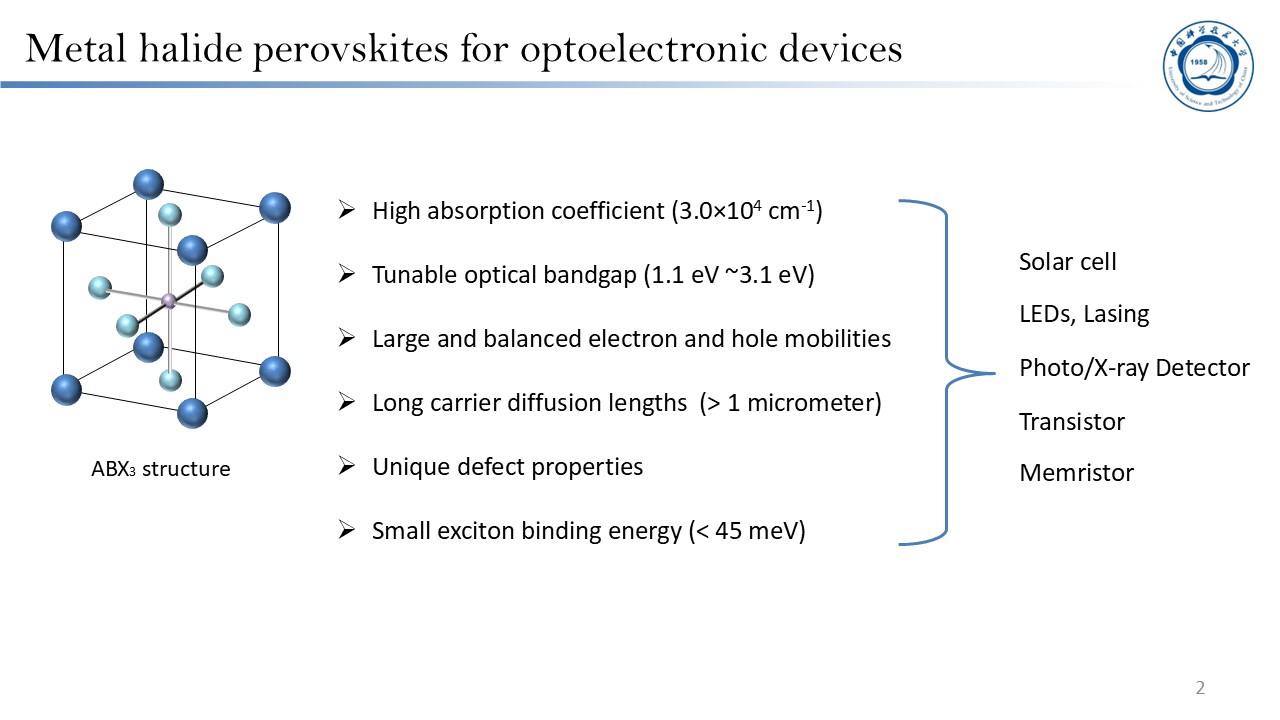
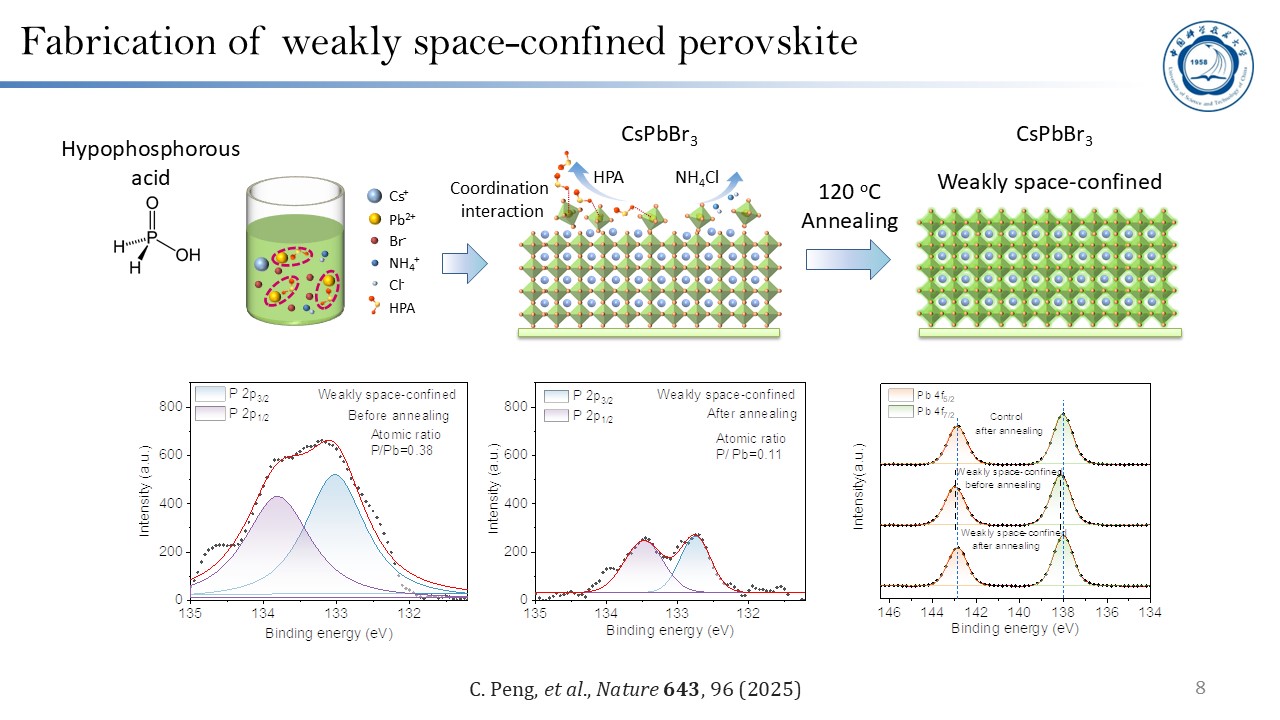
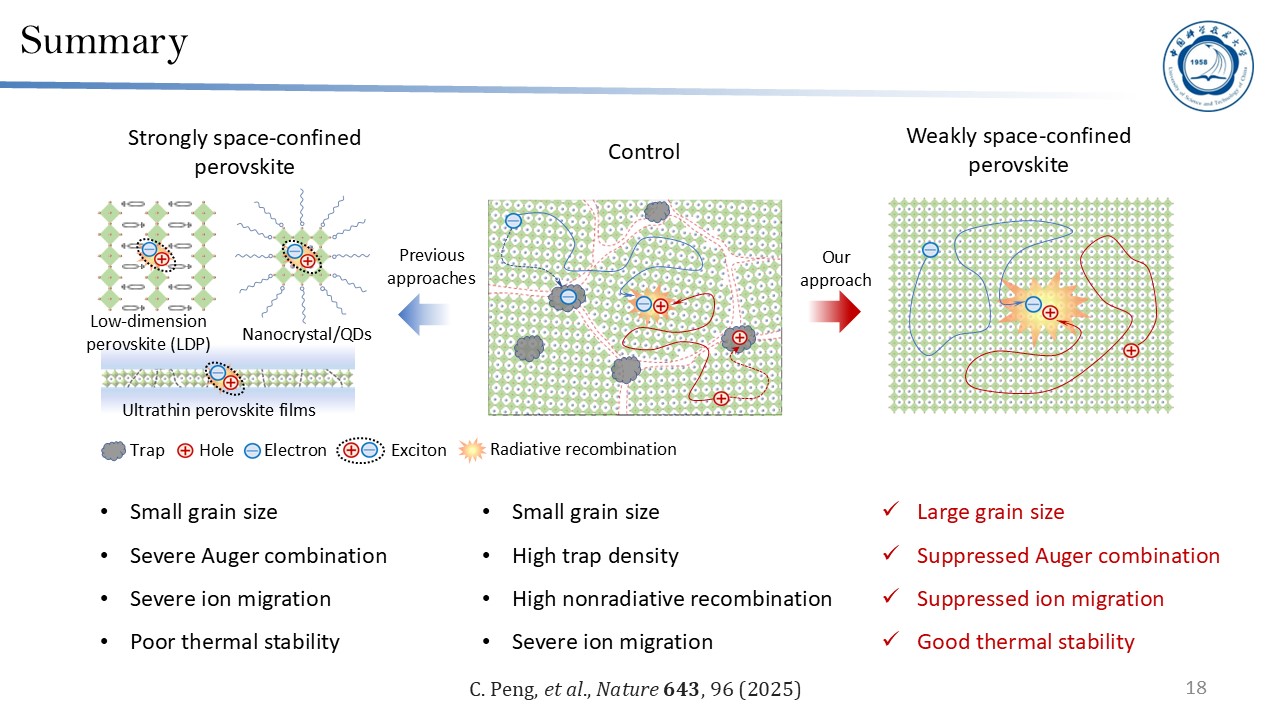
The author highlights his group's research, focusing on developing high-efficiency and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes (PeLEDs), with particular emphasis on exploring a new approach to improve the efficiency and lifetime through a “weak space-confinement” strategy. Although the conventional “strong space-confinement” strategy can improve emission efficiency, it also leads to severe Auger recombination and ion migration, resulting in low brightness and poor device stability of perovskite LEDs. Moreover, the commonly used organic ligands in such systems exhibit poor thermal stability and cannot withstand Joule heating during device operation, thereby limiting the long-term stability. To overcome these challenges, hypophosphorous acid (HPA) and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) were introduced into the CsPbBr3 precursor system to regulate the crystallization process. This approach yielded highly crystalline perovskite films with large grain size and low grain-boundary density. The weakly space-confined perovskite films show suppressed Auger recombination, reduced ion migration, and enhanced thermal stability. Based on this design, the fabricated green PeLEDs achieved an external quantum efficiency (EQE) of 22%, a maximum brightness of 1.16×106 cd m-2, and an extrapolated lifetime of 1.85×105 hours at 100 cd m-2. These results represent a significant breakthrough in both brightness and stability, providing a promising pathway toward the practical application of perovskite LEDs.
We acknowledge support from the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2022YFA1204800), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (62175226, 62234004, 52302201), the University Synergy Innovation Program of Anhui Province (GXXT-2022-009), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2022M723006), and a fellowship from the China National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents (BX20230353).
1. C. Peng, H. Yao, O. Ali, W. Chen, Y. Yang, Z. Huang, H. Liu, J. Li, T. Chen, Z. Li, M. Sun, H. Zhou, X. Tao, N. Wang, J. Wang, and Z. Xiao, Weakly space-confined all-inorganic perovskites for light-emitting diodes, Nature 643, 96 (2025).
2. Z.K. Tan, R.S. Moghaddam, M.L. Lai, P. Docampo, R. Higler, F. Deschler, M. Price, A. Sadhanala, L.M. Pazos, D. Credgington, F. Hanusch, T. Bein, H.J. Snaith, and R.H. Friend, Bright light-emitting diodes based on organometal halide perovskite, Nat. Nanotechnol. 9, 687 (2014).
3. H. Cho, S.H. Jeong, M.H. Park, Y.H. Kim, C. Wolf, C.L. Lee, J.H. Heo, A. Sadhanala, N. Myoung, S. Yoo, S.H. Im, R.H. Friend, and T.W. Lee, Overcoming the electroluminescence efficiency limitations of perovskite light-emitting diodes, Science 350, 1222 (2015).
4. M. Yuan, L.N. Quan, R. Comin, G. Walters, R. Sabatini, O. Voznyy, S. Hoogland, Y. Zhao, E.M. Beauregard, P. Kanjanaboos, Z. Lu, D.H. Kim, and E.H. Sargent, Perovskite energy funnels for efficient light-emitting diodes, Nat. Nanotechnol. 11, 872 (2016).
5. N. Wang, L. Cheng, R. Ge, S. Zhang, Y. Miao, W. Zou, C. Yi, Y. Sun, Y. Cao, R. Yang, Y. Wei, Q. Guo, Y. Ke, M. Yu, Y. Jin, Y. Liu, Q. Ding, D. Di, L. Yang, G. Xing, H. Tian, C. Jin, F. Gao, R.H. Friend, J. Wang, and W. Huang, Perovskite light-emitting diodes based on solution-processed self-organized multiple quantum wells, Nat. Photonics 10, 699 (2016).
6. Z. Xiao, R.A. Kerner, L. Zhao, N.L. Tran, K.M. Lee, T.W. Koh, G.D. Scholes, and B.P. Rand, Efficient perovskite light-emitting diodes featuring nanometre-sized crystallites, Nat. Photonics 11, 108 (2017).
7. Y. Dong, Y.K. Wang, F. Yuan, A. Johnston, Y. Liu, D. Ma, M.J. Choi, B. Chen, M. Chekini, S.W. Baek, L.K. Sagar, J. Fan, Y. Hou, M. Wu, S. Lee, B. Sun, S. Hoogland, R. Quintero-Bermudez, H. Ebe, P. Todorovic, F. Dinic, P. Li, H.T. Kung, M.I. Saidaminov, E. Kumacheva, E. Spiecker, L.S. Liao, O. Voznyy, Z.H. Lu, and E.H. Sargent, Bipolar-shell resurfacing for blue LEDs based on strongly confined perovskite quantum dots, Nat. Nanotechnol. 15, 668 (2020).
8. D. Ma, K. Lin, Y. Dong, H. Choubisa, A.H. Proppe, D. Wu, Y.K. Wang, B. Chen, P. Li, J.Z. Fan, F. Yuan, A. Johnston, Y. Liu, Y. Kang, Z.H. Lu, Z. Wei, and E.H. Sargent, Distribution control enables efficient reduced-dimensional perovskite LEDs, Nature 599, 594 (2021).
9. J.S. Kim, J.M. Heo, G.S. Park, S.J. Woo, C. Cho, H.J. Yun, D.H. Kim, J. Park, S.C. Lee, S.H. Park, E. Yoon, N.C. Greenham, and T.W. Lee, Ultra-bright, efficient and stable perovskite light-emitting diodes, Nature 611, 688 (2022).
10. Y.H. Kim, S. Kim, A. Kakekhani, J. Park, J. Park, Y.H. Lee, H. Xu, S. Nagane, R.B. Wexler, D.H. Kim, S.H. Jo, L. Martínez-Sarti, P. Tan, A. Sadhanala, G.S. Park, Y.W. Kim, B. Hu, H.J. Bolink, S. Yoo, R.H. Friend, A.M. Rappe, and T.W. Lee, Comprehensive defect suppression in perovskite nanocrystals for high-efficiency light-emitting diodes, Nat. Photonics 15, 148 (2021).
11. Y. Jiang, M. Cui, S. Li, C. Sun, Y. Huang, J. Wei, L. Zhang, M. Lv, C. Qin, Y. Liu, and M. Yuan, Reducing the impact of Auger recombination in quasi-2D perovskite light-emitting diodes, Nat. Commun. 12, 336 (2021).
12. S. Yuan, L. Dai, Y. Sun, F. Auras, Y.H. Zhou, R.Z. An, Y. Liu, C. Ding, C. Cassidy, X. Tang, S.C. Dong, H.B. Kang, K. Chen, X. Liu, Z.F. Ye, Y. Zhao, C. Adachi, L.S. Liao, N.C. Greenham, Y. Qi, S.D. Stranks, L.S. Cui, and R.H. Friend, Efficient blue electroluminescence from reduced-dimensional perovskites, Nat. Photonics 18, 425 (2024).



